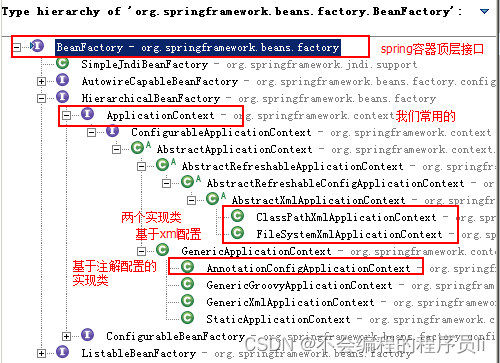
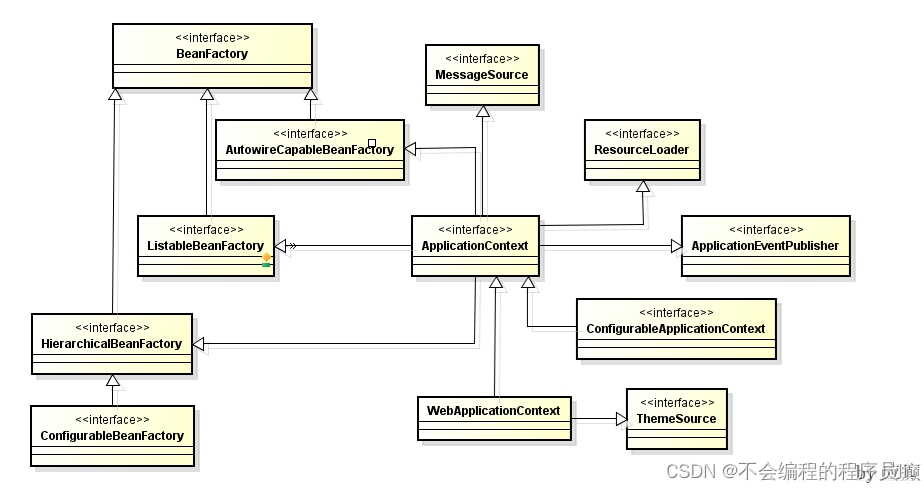
BeanFactory 与 ApplicationContext 区别 BeanFactory 是 Spring 框架中 IoC 容器的顶层接口,它只是用来定义一些基础功能,定义一些基础规范,而 ApplicationContext 是它的一个子接口,所以 ApplicationContext是具备 BeanFactory 提供的全部功能的。
使用 Spring IoC 容器的方式 XML 方式 xml 文件头 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" ></beans >
实例化Bean的三种方式
使用无参构造函数
1 2 3 4 <bean id ="accountDao" class ="com.lagou.edu.dao.impl.JdbcAccountDaoImpl" /> <bean id ="transferService" class ="com.lagou.edu.service.impl.TransferServiceImpl" > <property name ="AccountDao" ref ="accountDao" /> </bean >
使用静态方法创建
1 <bean id ="connectionUtils" class ="com.lagou.edu.utils.ConnectionUtils" factory-method ="getInstance" />
使用实例化方法创建
1 2 <bean id ="createBeanFactory" class ="com.lagou.edu.factory.CreateBeanFactory" /> <bean id ="connectionUtils2" factory-bean ="createBeanFactory" factory-method ="getInstant" />
Bean 标签属性
在基于 xml 的 IoC 配置中,bean 标签是最基础的标签。它表示了 IoC 容器中的一个对象。换句话说,如果一个对象想让 spring 管理,在 XML 的配置中都需要使用此标签配置,Bean 标签的属性如下:
id属性:用于给bean提供一个唯一标识。在一个标签内部,标识必须唯一。
class属性:用于指定创建Bean对象的全限定类名。
name属性:用于给bean提供一个或多个名称。多个名称用空格分隔。
factory-bean属性:用于指定创建当前bean对象的工厂bean的唯一标识。当指定了此属性之后, class属性失效。
factory-method属性:用于指定创建当前bean对象的工厂方法,如配合factory-bean属性使用, 则class属性失效。如配合class属性使用,则方法必须是static的。
scope属性:用于指定bean对象的作用范围。通常情况下就是singleton。当要用到多例模式时, 可以配置为prototype。
init-method属性:用于指定bean对象的初始化方法,此方法会在bean对象装配后调用。必须是 一个无参方法。
destory-method属性:用于指定bean对象的销毁方法,此方法会在bean对象销毁前执行。它只 能为scope是singleton时起作用。
DI 依赖注入的 XML 配置 依赖注入分类
按照注入的方式分类 构造函数注入:利用带参构造函数实现对类成员的数据赋值,使用标签 constructor-arg
name:用于给构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值
index:用于给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值
value:用于指定基本类型或者 String 类型的数据
ref:用于指定其他 bean 类型的数据,写的是其他 bean 的唯一标识
set 方法注入:它是通过类成员的 set 方法实现数据的注入,使用标签 property
name:指定注入时调用的set方法名称。(注:不包含set这三个字母)
value:指定注入的数据。它支持基本类型和String类型
ref:用于指定其他 bean 类型的数据,写的是其他 bean 的唯一标识
按照注入的数据类型分类
基本类型和 String:注入的数据类型是基本类型或者是字符串类型的数据
其他 bean 类型:注入的数据类型是对象类型,这个对象要求在 IoC 容器中
复杂类型(集合类型)
注入的数据类型是 Aarry,List,Set,Map,Properties 中的一种类型。
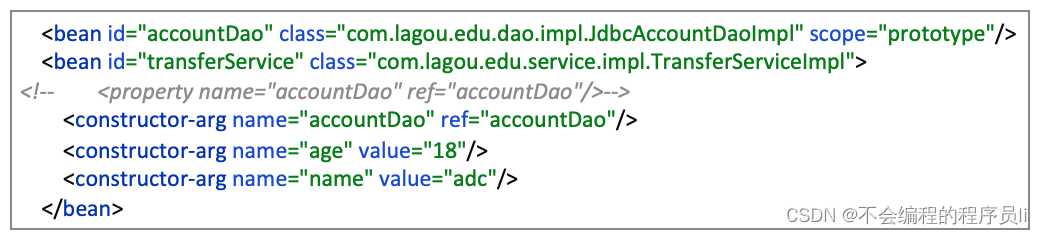
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 <bean id ="transferService" class ="com.lagou.edu.service.impl.TransferServiceImpl" > <constructor-arg name ="accountDao" ref ="accountDao" /> <constructor-arg name ="age" value ="18" /> <constructor-arg name ="name" value ="adc" /> <property name ="myArray" > <array > <value > arr1</value > <value > arr2</value > <value > arr3</value > </array > </property > <property name ="myMap" > <map > <entry key ="key1" value ="value1" /> <entry key ="key2" value ="value2" /> <entry key ="key3" value ="value3" /> </map > </property > <property name ="mySet" > <set > <value > set1</value > <value > set2</value > <value > set3</value > </set > </property > <property name ="myProperties" > <props > <prop key ="key1" > value1</prop > <prop key ="key2" > value2</prop > <prop key ="key3" > value3</prop > </props > </property > </bean >
在 List 结构的集合数据注入时,array , list , set 这三个标签通用,另外注值的 value
XML 与注解结合的方式 引入:
实际企业开发中,纯 xml 模式使用已经很少了
引入注解功能,不需要引入额外的 jar
xml+注解结合模式,xml 文件依然存在,所以 Spring IoC 容器的启动仍然从加载 xml 开始
第三方 jar 中的 bean 定义在 xml,比如 druid 数据库连接池。自己开发的 bean 定义使用注解
xml 中标签与注解的对应
xml 形式
对应的注解形式
标签
@Component(“accountDao”),注解加在类上 bean 的 id 属性内容直接配置在注解后面如果不配置,默认定义个这个 bean 的 id 为类的类名首字母小写。另外,针对分层代码开发提供了 @Componenet 的三种别名 @Controller、 @Service、@Repository 分别用于控制层类、服务层类、dao 层类的 bean 定义,这四个注解的用法完全一样,只是为了更清晰的区分而已
标签的 scope 属性
@Scope(“prototype”),默认单例,注解加在类上
标签的 init-method 属性
@PostConstruct,注解加在方法上,该方法就是初始化后调用的方法
标签的 destory-method 属性
@PreDestory,注解加在方法上,该方法就是销毁前调用的方法
xml 里需要配置注解扫描 引入Spring Context 命名空间
xmlns:context=”http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation =" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.lagou.edu" /> <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" /> </bean > </beans >
DI 依赖注入的注解实现方式 @Autowired
1 2 @Autowired private AccountDao accountDao;
如上代码所示,这样装配回去 Spring 容器中找到类型为 AccountDao 的类,然后将其注入进来。这样会产生一个问题,当一个类型有多个 bean 值的时候,会造成无法选择具体注入哪一个的情况,这个时候我们需要配合着 @Qualifier 使用。
@Qualifier 告诉 Spring 具体去装配哪个对象
1 2 3 @Autowired @Qualifier("jdbcAccountDaoImpl") private AccountDao accountDao;
@Resource
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class TransferService { @Resource private AccountDao accountDao; @Resource(name="studentDao") private StudentDao studentDao; @Resource(type="TeacherDao") private TeacherDao teacherDao; @Resource(name="manDao",type="ManDao") private ManDao manDao; }
如果同时指定了 name 和 type,则从 Spring 上下文中找到唯一匹配的 bean 进行装配,找不到则抛出异常。
如果指定了 name,则从上下文中查找名称(id)匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常。
如果指定了 type,则从上下文中找到类似匹配的唯一 bean 进行装配,找不到或是找到多个, 都会抛出异常。 如果既没有指定 name,又没有指定 type,则自动按照 byName 方式进行装配。
纯注解方式 将 xml 中的配置以注解的形式迁移到配置类中即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.lagou.edu"}) @Import({DataSourceConfig.class}) public class SpringConfig {}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @PropertySource({"classpath:jdbc.properties"}) public class DataSourceConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driverClassName; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource () { DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource (); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(password); return dataSource; } }
对应注解 @Configuration :表名当前类是一个配置类@ComponentScan :替代 context:component-scan@PropertySource :引入外部属性配置文件@Import :引入其他配置类@Value :对变量赋值,可以直接赋值,也可以使用 ${} 读取资源配置文件中的信息 @Bean:将方法返回对象加入 SpringIoC 容器
启动 IoC 容器的方式 Java 环境下启动 IoC 容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类的根路径下加载配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从磁盘路径上加载配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 public void test () { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("application-context.xml" ); TransferService transferService = (TransferService) applicationContext.getBean("transferService" ); System.out.println(transferService); }
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:纯注解模式下启动 Spring 容器
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void test () { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (SpringConfig.class); TransferService transferService = (TransferService) applicationContext.getBean("transferServiceImpl" ); System.out.println(transferService); }
Web 环境下启动 IoC 容器 从 xml 启动容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app > <display-name > Archetype Created Web Application</display-name > <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:application-context.xml</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > </web-app >
从配置类启动容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app > <display-name > Archetype Created Web Application</display-name > <context-param > <param-name > contextClass</param-name > <param-value > org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext</param-value > </context-param > <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > com.lagou.edu.SpringConfig</param-value > </context-param > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > </web-app >
servlet 中获取容器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @WebServlet(name = "transferServlet", urlPatterns = "/transferServlet") public class TransferServlet extends HttpServlet { private TransferService transferService; @Override public void init () throws ServletException { WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext( this .getServletContext()); TransactionProxyFactory transactionProxyFactory = webApplicationContext.getBean(TransactionProxyFactory.class); this .transferService = transactionProxyFactory.getTarget(webApplicationContext.getBean(TransferService.class)); } @Override protected void doGet (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { } @Override protected void doPost (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { } }
SpringContextUtil——获取spring中的bean对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 @Component public class SpringContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("执行ApplicationContext对象注入!" ); SpringContextUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext () { return applicationContext; } public static <T> T getBean (Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException { return applicationContext.getBean(requiredType); } public static Object getBean (String name) throws BeansException { return applicationContext.getBean(name); } public static <T> T getBean (String name, Class<T> requireType) throws BeansException { return applicationContext.getBean(name, requireType); } public static boolean containsBean (String name) { return applicationContext.containsBean(name); } public static boolean isSingleton (String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { return applicationContext.isSingleton(name); } public static Class getType (String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { return applicationContext.getType(name); } public static String[] getAliases(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { return applicationContext.getAliases(name); } }